What is a refresh rate?
When comparing the screens of tech devices, you may find that different products offer different refresh rates for their screens. This article explains what that means for you.
There are so many buzzwords relating to screens that it can be hard to keep track of them all, from LCD to OLED, from HDR to 10-bit. This article explains just what is meant by refresh rate, whether it be 60Hz, 90Hz, 120Hz or even 144Hz.
What is a refresh rate?
At its simplest, a refresh rate is the frequency at which a display updates itself. This quality is measured in Hertz, which represents the frequency per second; so a standard 60Hz panel updates itself sixty times every second, while a 120Hz panel updates itself twice as often, at one hundred and twenty times per second.
The advantage of a display with a higher refresh rate is displayed content can seem smoother to the human eye. If you’re watching fast-moving content such as a high-spec video game, or just scrolling swiftly down a social media feed, then a high refresh rate should make that process appear far more slick and natural rather than appearing to flicker slightly. That’s why an enhanced refresh rate is perceived as a premium feature on a smartphone or a monitor.
Note that this maximum smoothness, especially where games are concerned, needs to be achieved in tandem with a capable processor and suitable system requirements. What’s more, not all games or apps care capable at running at higher refresh rates, even if your device’s display would be able to support it.

What is a fixed refresh rate?
While higher refresh rates can deliver smoother results for compatible content, there’s another distinction between types of refresh that is crucially important when you’re making your purchase decision.
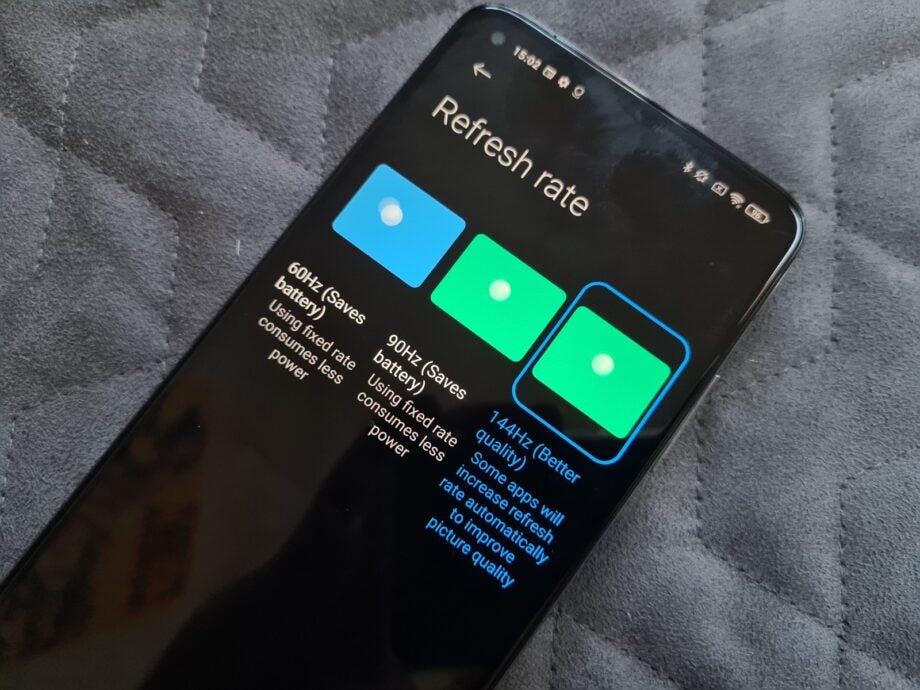
If a screen has a fixed refresh rate, this means that it will always apply that level of intensity even when the content playing on the screen does not update at the same frequency. So you might be using an app or game that tops out at 60Hz, but if the device’s refresh rate is set at 120Hz then it will continue to apply this setting in vain. Some screens with fixed refresh rates may enable you to manually change the settings – as in the above picture of a smartphone, where you can choose between 60Hz or 120Hz – but the device will not be able to automatically adapt depending on the content displayed on the screen.
What is a variable refresh rate?
In contrast to the above, an adaptive refresh rate will automatically adjust itself to fit the content that is playing on screen, within a predefined limit.
Take the example of using a 120Hz smartphone display that is adaptive to 1Hz. If you’re playing a high-spec video game on its maximum settings then it will deliver the full 120Hz maximum so that it’s as smooth as can be; but if the display is showing static content then it can run on a 1Hz refresh rate, in order to use as little power as possible. This means that devices with a variable refresh rate can deliver enhanced smoothness when possible, while also being more energy efficient for the sake of battery life.
What is a touch sampling rate?
You may also have noticed that a refresh rate is not the only screen-related feature than is measured in Hertz; there’s also a quality named touch sampling that uses the same unit. Once again this also describes the number of times an action is performed per second, but in this content it’s the frequency that a touchscreen display refreshes itself in order to register a user’s touch input.
For instance, a display with 240Hz touch sampling is refreshed two hundred and forty times per second and is highly sensitive to user input. That’s ideal when you’re playing competitive games on your smartphone, where every second counts.